Electrical Wiring
Electrical
wiring is an electrical installation of
cabling and associated devices such as switches, distribution boards, sockets,
and light fittings in a structure.
Wiring is subject to safety standards for design and installation. Allowable wire and cable types and sizes are specified according to the circuit operating voltage and electric current capability, with further restrictions on the environmental conditions, such as ambient temperature range, moisture levels, and exposure to sunlight and chemicals.
Associated circuit protection, control and distribution devices within a building's wiring system are subject to voltage, current and functional specification. Wiring safety codes vary by locality, country or region. The International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) is attempting to harmonize wiring standards amongst member countries, but significant variations in design and installation requirements still exist.
Methods of Electrical Wiring
There are mainly five
types of wiring which are discussed below:
Cleat wiring: Electric wiring on cleats or insulated supports which are mounted on a wall or other surface, leaving the wiring exposed. They are held on walls and ceilings using porcelain cleats with groves, wood or plastic. It is a temporary wiring system, therefore making it unsuitable for domestic premises. Moreover, cleat wiring system is rarely being used these days.
Casing and Capping Wiring: As the name referred in this wiring, PVC insulated wires are placed in plastic cashing and covered with cap. The cashing is of rectangular cross section. The color of cashing channel and cap are normally white or grey. It was quite popular in the past but it is considered obsolete these days due to the popularity of the conduit and sheathed wiring system.
Batten Wiring:
In batten wiring,
the insulated wires are
placed on the batten, in a
straight manner. The battens are
fixed on the wall or the ceiling with the help of plugs or screws.
Lead Sheathed
Wiring: This type of wiring employs
conductors insulated with VIR and is covered with an outer sheath of lead-aluminum alloy containing about
95% lead. This metal sheath gives protection to the
cable from mechanical injury, dampness and atmospheric corrosion.
Conduit
Wiring: An electrical conduit is
a tube used to protect and route electrical wiring in a building or structure. Electrical conduit may be made of metal,
plastic, fiber, or fired clay. Most conduit is rigid, but flexible conduit is used for some purposes.
Service Drop Cable
It is the cable
between the utility pole and the consumer’s premises or building. The service
drop cable is an overhead electrical line from the pole to the service weather
head of a house.
The service drop cable can be of many types given below:
•
Duplex Cable
•
Triplex
Cable
• Quadruple Cable
Color Coding in Wires
Color coding of cable
insulation is done to determine active, neutral and earth conductors.
Different
countries/regions have different cable color coding, and it is essential to
know what is applicable in your region.
Given figure shows
color coding for ‘Bharat’.
Sizes of Wires
Electrical wire size
is sold in square mm unit in India. Electrical wires sizes start from 1.0 Sq.
mm and can go up to 6 Sq. mm for domestic / home purposes.
The area given above in the table is the table is the cross-sectional area of the wire.
Wire Lettering
Other than color on
wires, lettering is done on wires to distinguish between them. The letters THHN, THWN, THW AND XHHN etc.
represents the main insulation types of individual wires.
•
T – Thermoplastic insulation
•
H – Heat resistance
•
HH – High Heat Resistance (up to 194 deg. F)
•
W – Suitable for wet locations
•
N – Nylon coating, resistant to damage by oil &
gas
•
X – Synthetic polymer that is flame-resistant
The
letter THHN written on the box means
the wire inside is with thermoplastic insulation, high heat resistant and of
nylon coating for protection from oil and gas.
General Guidelines for Placement of Socket & Switches
•Electrical Socket outlets provided for appliances such
as air conditioners, water coolers, washing machines etc. that
use electricity up to 16A, shall be provided with its own fuse with
suitable backup fuse or miniature circuit breaker.
•The switch controlling the socket outlet shall be on
the live side of the line.
•For earthing purpose, the socket shall be of 3 pin
with the third terminal connected to the earth wire.
•Earth wire must be insulated properly so that there is
no leakage of current otherwise it can cause savior damage.
•In wiring installations, metal clad switch, socket- outlet
and plugs shall be used for power wiring.
•Controlling of ceiling fan shall be through its own
regulator as well as a switchboard.
•Switchboards for outdoor lamps and verandah lamps must
be provided separately.
•A switch shall be provided for the control of every
light fixture or a group of light fitting fixtures.
Basic Household Electrical Fixtures
Electrical Meter
It is used to measure the units of electrical energy used in your household circuits.
There are two types of electrical meters given below:
- Electromechanical meter
- Electronic/Digital meter
Electromechanical meters were very common in India a few years ago but no more. The working of electromechanical meters is fairly simple. There is a non-magnetic metallic disc attached to it internally which rotates depending upon the power passing through it.
Electronic meters are becoming increasingly popular nowadays. An electronic meter has a LED/LCD display on which the readings of the electricity consumption of the connected appliances. The readings are digital in the electronic meters in contrast to the electromechanical meters. These are much more efficient than the electromechanical meters in the sense that they do register every small unit of electricity consumed.
Electricity provider uses meter readings to create your electricity bill every 30-45 days or so.
Electromechanical meter Electronic/Digital meter
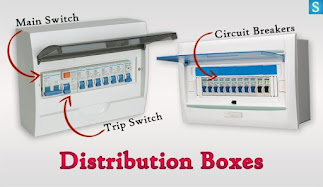
Distribution Box
Distribution box is very easy to notice (electrical fixture) in your home. It consists 3 more electrical parts, namely:
- Main Switch (MCCB – Moulded Case Circuit Breaker)
- Trip Switch (RCCB – Residual Current Circuit Breaker)
- Circuit Breakers (CBs )
As the name implies,
Distribution Box simply distributes the electric supply to sections of the
house. These sections contain light circuits [Light Switches + Light
Bulbs], fan circuits [Fan Regulator + Fan]
and plug socket circuits etc.
Main Switch (MCCB)
Moulded Case Circuit
Breaker (MCCB) can easily be found in the distribution box of your home or any
building. It is the first electrical part receiving the electricity from the
electric meter inside your house. Therefore, the Main Switch is the responsible
part to take down the electricity throughout the house as required.
There are 2 wires
inside the cable coming from the electric meter namely Live Wire and Neutral Wire. These 2 wires are then
connected to the Main Switch. While the main switch is OFF the electric supply
is stopped by disconnecting the two wires.
Trip Switch or RCCB (Residual Current Circuit Breaker) and Fuse
The distribution box will either have fuses or trip switches. Modern electric circuits are fitted with a circuit breaker fuse system; if a fault develops, a switch is tripped and the circuit is broken. Older ones have fuse holders and when a fuse is blown it must be replaced or rewired.
Trip switches are basically fuses; when too much current (load) passes through a given circuit the switch is 'tripped' and the circuit is broken.
Fuses used in inverter Old Fuses RCCB/Trip Switch
Basically fuses are
used to protect electrical appliances, parts and electronic components from potential
damage due to a high current flowing in the circuit.
This electrical part is a small length thin wire created using lead and tin alloy. There are different fuse wires with the ability to conduct certain maximum currents such as 1A, 2A, 3A, 6A, 10A and 16A.
Wall Sockets
There are plug sockets
to get 6A, 13A or 16A current.
There are two types of Plug Sockets based on pin type such as two-pin plugs and
three-pin plugs where the 3rd pin is for Earth Wire. To get these
connections, electricians use two core wires and three core wires.
Plug Sockets come with
a cap inside for extra protection, so you don’t get electrocuted or harm your
appliances while plugging. Wall Sockets are always used with a switch. For
safety, you need to OFF the switch before plugging any plugs.
Wall Switches/Keys
Wall Switches are
among the top consumed electrical parts list in any place that uses
electricity. Switches are used in light circuits and plug socket circuits to
connect or disconnect the circuit.
There are single,
double, triple, quadruple as well as quintuple wall switches.
Electricians can attach multiple lights to a single switch as long as the current rating of the switch is not exceeded, for example all outdoor lights can be attached to a single switch letting you light up them at once easily.
Wall Switches
Two Way Switches
These switches are
used to operate a light from two different places.
For example, you ON
the switch while you inside the house and then you lock the door once outside. Now
you want to OFF the switch, how do you do that? You setup a Two Way switch
outside the house and you OFF it there.
Two Way switch circuit
*If you have any query, then comment it down.



















Comments
Post a Comment
If you have any doubt. Please let me know.